Flat Rolled Low Carbon Sheet
If you are new to the steel industry or just need a refresher, MVSS is pleased to offer the following information to make your job easier. Let us know if you have any questions, we are here to help.
Click here to download the Steel 101 presentation
Sections
Steel Mill Types | Common Steel Types | Common Types of Coated Steel | Chemistry | Steel Grades and Hardness | Steel Strength (Mechanical Properties) | | Steel Supply Chain
steel \ˈstēl\
A generally hard, strong, durable, malleable alloy of iron and carbon, usually containing between 0.2 and 1.5 percent carbon.
Steel Mill Types
There are different types of flat rolled steel mills:
Integrated Mills | Mini Mills | Conversion Mills
Integrated Mills: The principal raw materials for an integrated mill are iron ore, limestone, scrap, and coal (or coke). These materials are charged in batches in a blast furnace where the raw materials are converted to liquid iron (also called pig iron). The material is then moved to a basic oxygen furnace (BOF) for final chemistry refinement. Material is poured into a thick slab and is cooled for future rolling. Slabs must be reheated in ovens to be rolled down to a final thickness.
Advantages: generally produces broader grades and types of steel than mini mills.
Examples:
- Arcelor Mittal
- AK Steel
- US Steel
- Essar Algoma
Mini Mills: Obtains most of its iron from scrap steel recycled from used automobiles and equipment or by-products of manufacturing. Material is melted in an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF). Material is continuously cast from the laddle into a slab form and while still heated is rolled to a final sheet product.
Advantages:
- Newer and efficient infrastructure
- Uses recycled material- more Eco friendly
- Reduced energy costs than other types of mills
- Less labor required
- Produces less pollution
- Reduced leadtimes
- Improved gauge control
Examples:
- Steel Dynamics (SDI)
- Nucor
- North Star BlueScope Steel
- Big River
- NLMK Indiana
Conversion Mills: Convert slabs into flat rolled coils by heating them up and reducing gauge through rolling mills.
Advantages:
- Leadtimes
- Smaller min order quantity
- Flexibility on size / width of coils
Examples:
- NLMK PA
- Wheeling Nisshin
- AM/NS-Calvert (Arcelor Mittal / Nippon Steel)
- CSN
Common Steel Types
Hot Rolled (Hot Rolled Black) : molten steel that is cooled and formed into coils while steel is red hot (approx. 1,700°). Product has scale , which is a oxide coating that is formed at high temperatures. Rust forms on unprotected metal and is often stored outside.


Hot Rolled Pickled & Oiled (HR P&O): Hot rolled black is uncoiled and sent through a series of hydrochloric baths that removes scale, rust, and unwanted debris. The coil is then lightly oiled for temporary rust prevention.


Cold Rolled Steel (CR):
Is produced by running HRP&O steel through a series of rollers at room temperature to reduce thickness. The rolling process can increase strength and improve surface finish.
When reducing gauge by a large percentage the material becomes brittle and hard and must go through an annealing (baking) and tempering process to regain formability and required hardness.
Common Types of Coated Steels:
Electro-Galvanized (EG/EL):Zinc plating process whereby the molecules on the positively charged zinc anode attach to the negatively charged sheet steel. Thickness of coating can be readily controlled by electric charge or changing the speed of operation.
Great surface for painting and precise coating thicknesses
Applications: Automotive (electrical components, body panels) and Appliance (dishwashers/ stoves etc.)
Galvanized (GA): Hot dipped galvanized is manufactured by passing steel through a molten bath of zinc to form a thin layer of corrosion resistance. Leaves a crystallization pattern on surface called spangle.
Uses: HVAC & Construction
Galvanneal (GN): Is produced by taking a hot dipped galvanized coil and passing it through a series of furnaces that raise the temperature so that iron atoms from the sheet move into the zinc coating to form a zinc-iron layer.
Great surface for painting and a lower cost alternative to Electro- Galvanized.
Applications: Mainly automotive (Hoods, Doors, and Body Panels)
Aluminized (AZ): Steel that has been hot-dip coated with aluminum-silicon alloy (T1) or pure aluminum (T2).
Type 1 (T1): Heat Resistant, better formability than T2, generally thinner coating thicknesses than T2.
Uses: automotive exhaust systems and ovens
Type 2 (T2): High Corrosion Resistance
Uses: construction (Example- Road Culvert Pipe)
Chemistry
primary elements added to Iron, below are percentages
| SAE Certs | Carbon | Manganese | Phosphorous | Sulfur |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1006 | 0 - .08 | 0 - .45 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 |
| 1008 | 0 - .10 | 0 - 0.50 | 0 - .03 | 0 - 0.5 |
| 1008/1010 | 0 - .13 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 |
| 1010 | .08 - .13 | .30 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 -.035 |
| 1018 | .15 - .20 | .60 - .90 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 |
| 1018/1020 | .15 - .23 | .60 -.90 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 |
| 1020 | .18- .23 | .30 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 |
Steel Grades and Hardness
Steel Grades:
- CS (CQ): Commercial Steel
- DS (DQ) or FS: Drawing Steel or Forming Steel (Coated Products)
- DDS (DDQ): Deep Drawing Steel
- EDDS: Extra Deep Drawing Steel
- SS: Structural Steels
- HSLA: High Strength Low Alloy Steels
Rockwell B Scale (Rb):
is a hardness scale based on the surface hardness of a material. Scale is 0 to 100, higher the Rb harder the material. Used for Aluminum, brass, and soft steels.
(Rockwell C Scale is used for harder steels)
Steel Grades and Hardness
ASTM Guidelines for Grades of Steel**
(For reference only)
Commonly Used Steel Types
Cold Rolled (CR) A1008
| Rb max | C | Mn | P | S | AI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS Type A | 65 | 0 - .10 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| CS Type B | 65 | .02 - .15 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| DS Type A | 55 | 0 - .08 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .03 | .01 min |
| DS Type B | 55 | .02 - .08 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .03 | .02 min |
| DDS | 50 | 0 - .06 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .025 | .01 min |
| EDDS | 45 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .40 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .02 | .01 min |
Hot Rolled Pickled & Oiled A1011
| Rb max | C | Mn | P | S | AI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS Type A | 75 | 0 - .10 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| CS Type B | 75 | .02 - .15 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| DS Type A | 60 | 0 - .08 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .03 | .01 min |
| DS Type B | 65 | .02 - .08 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .03 | .01 min |
Galvanized Coated (GA) A653
| Rb max | C | Mn | P | S | AI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS Type A | 65 | 0 - .10 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| CS Type B | 65 | .02 - .15 | 0 - .60 | 0 - .03 | 0 - .035 | - |
| FS (DS) Type A | 55 | 0 - .10 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .035 | - |
| FS (DS) Type B | 55 | .02 - .10 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .03 | - |
| DDS | 50 | 0 - .06 | 0 - .50 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .025 | .01 min |
| EDDS | 45 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .40 | 0 - .02 | 0 - .02 | .01 min |
** for maximum amounts of: Cu, Ni, Cr, Mo, V, Cb, Ti, N, B please reference specific ASTM Specification.
Steel Strength (Mechanical Properties)
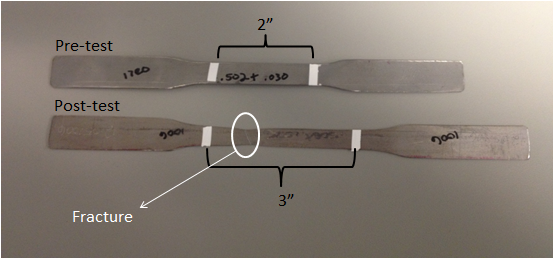
TYE or YTE:
Yield Strength:
The stress at which a material is permanently deformed.
Tensile (Ultimate Strength):
The maximum stress that a material can withstand without fracture
Elongation %:
Total amount of elongation (stretch) until fracture
“Dog Bone” samples showing results of TYE testing
Logistics through the Supply Chain
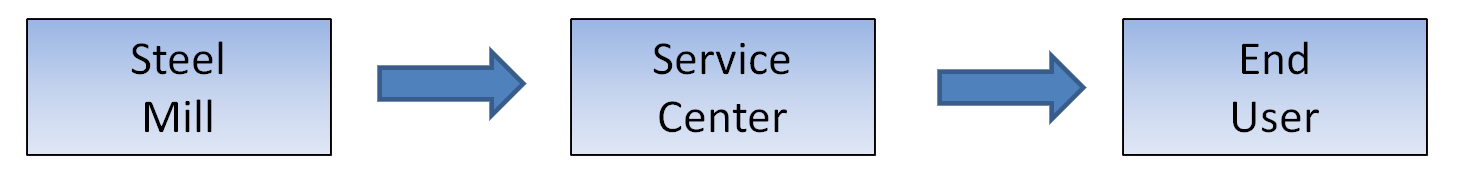
Why is a Steel Service Center Needed?
- Buys in bulk and can offer end user smaller quantities and cost savings.
- Converts master coils into precise widths and lengths needed by end user.
- Timely / JIT deliveries: 3-7 day turn around compared to 4-8 week mill leadtime.
Questions?
If you have any questions, please feel free to access our resources page, call, or email:
[email protected]
937-773-7127


